Overview of Topic Areas Covered in CRM-FM Training and Certification for Marketing, Sales, and Product Management Professionals
Introduction: On-Demand CRM and The New Marketing Model™ (Unit 1)
Objectives of this Training and Certification Program 1-2
On-Demand CRM: A Tool for Improving Productivity, Efficiency, and Measurability in Sales and Marketing 1-3
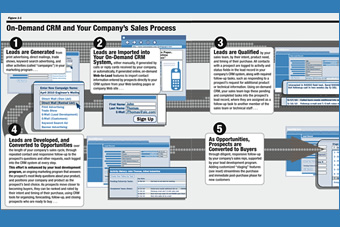
Figure 1-1: "CRM and Your Company's Sales Process," from
On-Demand CRM and The New Marketing Model (Unit 1)
Major Benefits of On-Demand CRM to the Business-to-Business Sales and Marketing Process 1-6
• Efficient New Processes Expose Old Inefficiencies 1-6
• Better Measurement is Contagious 1-7
• Often, the Problem Isn’t Lack of Measurement, It’s Poor Sales Response 1-7
Lead Development: After a Lead is Generated, It Must Be Developed, With the Help of Marketing Professionals 1-8
A Streamlined Process Becomes a Faster Process, Raising Expectations for Better Marketing Execution 1-10
The “Sales/Marketing Disconnect” 1-10
The New Marketing Model™ 1-11
On-Demand CRM and the New Marketing Model: Core Principles 1-12
1.) Knowledge of the Tradecraft of Marketing Execution 1-12
2.) Owning the Skills of Effective Marketing Execution 1-13
3.) Marketing Aligned with Sales 1-14
4.) Partnering with Sales by Executing Effective Lead Development Programs 1-15
5.) Using Clear Presentation in Lead Generation and Lead Development 1-17
6.) Using “Show What You Know” to Establish Thought Leadership and Unique Positioning for Your Company and Its Product 1-18
Functional Areas Where Marketing is Integrated With On-Demand CRM 1-18
1.) Tracking and Measuring Sales Response from Marketing Programs (On-Demand CRM Campaigns) 1-19
2.) Manual and Online Lead Capture (CRM Web-to-Lead); 1-21
3.) Online Storage and Distribution of Sales Support Marketing Deliverables (Marketing Documents) 1-21
4.) Executing, Tracking, and Measuring Lead Development Programs (Third-party E-Mailers and On-Demand CRM Reports) 1-22
5.) Produce, Execute, Measure, and Assess Keyword Search Advertising (On-Demand CRM and Google AdWords) 1-23
6.) Plan, Schedule, and Monitor Progress of Execution of Marketing Programs (CRM Project Management) 1-24
It All Starts With a Lead 1-24
On-Demand CRM and Your Marketing Plan: Integrating On-Demand CRM to Business-to-Business Marketing Programs, Methods, and Media (Unit 2)
Integrating Your Marketing Program and Aligning Its Objectives to On-Demand CRM 2-1
Two Essential Elements of Business-to-Business Marketing Plans in The New Marketing Model 2-4
How Marketing Tools and Media Integrate With On-Demand CRM 2-4
• Direct Mail 2-4
• Print Display Advertising 2-5
• Trade Shows 2-6
• Web Sites and Keyword Search Advertising 2-7
• E-Mail Message Programs 2-8
Field Marketing for Sales Support 2-8
Tracking and Measuring Response to Your Marketing
Program Using On-Demand CRM 2-10
Lead Tracking by Campaign in On-Demand CRM 2-10
Overview of Key Marketing Measurements Used in On-Demand CRM 2-12
• Response Rate 2-14
• Cost-per-Lead 2-14
• Return on Investment (ROI) 2-15
• Lifetime Value of a Customer 2-15
• Other Key Marketing Measurements 2-15
Marketing Professional’s Checklist for Creating a Campaign Using On-Demand CRM 2-17
1.) Creating a New Campaign 2-17
2.) Importing Leads to a Campaign 2-19
3.) Set up Campaign Tracking Features 2-19
4.) Export Leads or Contacts to a Mailing List (for Direct Mail Projects) 2-22
5.) Execute Your Campaign, and Track, Measure, and Assess Campaign Response 2-23
Marketer’s Action Plan: Six Steps to Effective Marketing Execution Utilizing Campaigns in On-Demand CRM 2-24
1.) Create Your Plan 2-25
2.) Plan for Measurement 2-26
3.) Execute 2-27
4.) Track, Measure, Monitor, and Assess 2-27
5.) Evaluate, Adapt, and Improve 2-28
6.) Follow Through 2-28
How this Workbook is Organized: Overview of Main Workbook Sections 2-29
Professional Development for Business-to-Business Marketing Professionals 2-30
How to Write Advertising (Or Manage Those Who Do): Discovering, Developing, and Presenting Your Product's Most Effective Sales Message (Unit 3)
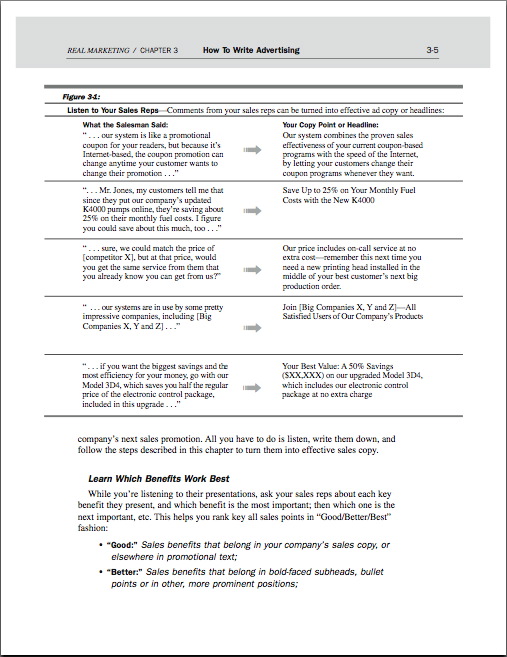
Figure 3-1: "Listen to Your Sales Reps," from Copywriting (Unit 3)
Effective Copywriting Means Research and Execution 3-2
• Part 1: The Information-Gathering Stage 3-3
• Step 1: Listen to Your Company’s Sales Reps 3-3
• How to Debrief a Sales Rep 3-4
• Learn Which Benefits Work Best 3-5
• How Do Your Salespeople Counter Common Sales Objections? 3-6
• What Else Do Your Salesmen Have to Say? (Plenty!) 3-6
Ask Your Top Sales Reps: “'What’s Your 'Elevator Pitch?'” 3-6
• Elevator Pitch Examples 3-7
• What Do Your Sales Reps Think of Your Company’s Marketing? 3-8
• Step 2: Check Your Competition 3-9
• Step 3: Get Your Competitor’s Sales Information Kit 3-9
• Step 4: Research Trade Publications in Your Industry 3-10
Part 2: Writing Effective Advertising and Promotional Copy 3-11
How Prospects See Your Advertising 3-11
Anatomy of an Effective Marketing Deliverable 3-12
• Headline 3-12
• Subheads 3-13
• Body Copy 3-14
• Call to Action 3-15
Writing Effective Advertising: Three Advertising Copywriting Exercises 3-16
Step 1: The Laundry List 3-16
• Sales Benefit Attributes 3-17
• Speed • Efficiency • Productivity 3-17
• Quality • Comprehensiveness • Richness 3-17
• Low cost • Savings • Value for money 3-18
• New • Updated • Improved • Upgraded • Different 3-19
Step 2: The Park Bench Story 3-19
Step 3: Your Elevator Pitch 3-21
• What You Have Accomplished by Completing these Exercises 3-21
Part 3: The Execution Stage 3-22
• Your Headline 3-23
• Converting Benefits to Headlines: Examples 3-23
• Your Subheads for Sales Copy 3-25
• Your Marketing Deliverable’s Body Copy 3-25
This Writing Process Opens Infinite Possibilities 3-27
Field Marketing Deliverables: Expedient Layout and Execution for Effective On-Demand CRM Sales and Marketing Documents (Unit 4)

Figure 4-5: "Landing Pages," from Field Marketing Deliverables (Unit 4)
Examples of Expedient Marketing Deliverables 4-2
1. Print Field Marketing Deliverables 4-3
• Informational Premiums 4-3
• White Papers 4-3
• Sales Support Materials 4-5
• Sales Flyers 4-5
• Comparison Charts: Powerful Marketing and Sales Tools 4-6
• Question-and-Answer/FAQ Sheets 4-9
Sales Letters 4-9
• Sales Letter Structure 4-10
• Sales Letter Idea Starters 4-11
• Step 1: Writing the Sales Letter Lead 4-11
• Lead With Empathy 4-11
• Ask a Question 4-12
• Start it Straight 4-12
• Break the News or Cite a Source 4-13
• Sometimes, a Headline Works Just Fine 4-13
• Sales Bullets and Key Sales Benefits 4-14
• Starting Your Body Copy 4-14
• Layout and Presentation Techniques for Sales Cover Letters 4-15
• Bullets 4-15
• Boldface Paragraph Leaders 4-16
• Boldface Phrases Within Paragraphs 4-16
• Copy Boxes 4-16
• Sales Letter Close and Call to Action 4-17
• The More Personal the Letter, the Less Promotional It Should Be 4-21
• Scouting New Deals and Filling Your Company’s Deal Pipeline Gives You a Place at the Table 4-22
2. Online Deliverables 4-22
• Landing Pages 4-22
• E-Mail Messages and Newsletter Formats 4-24
• Web Video 4-25
3. Other Marketing Deliverables 4-25
• Telephone Voicemail Scripts 4-25
• PowerPoint Presentations
• Checklist for Making PowerPoint Presentations More Effective 4-30
III: Expedient Layout Techniques for Field Marketing Deliverables 4-31
• Guiding Design Principles for Non-Designers 4-31
• Elements of Sales Flyers, Ads, and Other Promotional Marketing Deliverables 4-33
Design and Content Checklist for Effective Layout of Field Marketing Deliverables 4-36
• Layout Devices that Improve Presentation and Selling Power 4-40
Field Marketing Deliverables and On-Demand CRM Document Library Features 4-41
Direct Mail Planning: Generating Inquiries and Sales Leads Through Direct Mail and Direct Response (Unit 5)
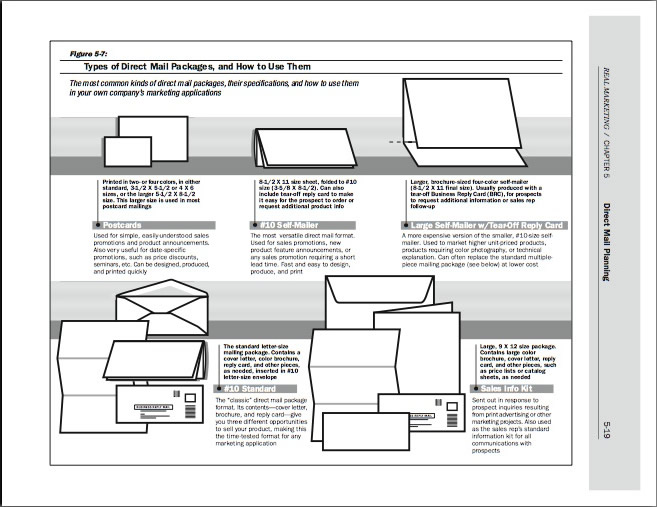
Figure 5-7 "Types of Direct Mail Packages, and How to Use Them," from Direct Mail Planning (Unit 5)
Advantages of Direct Mail 5-1
Direct Mail Applications 5-3
Part 1: Mailing Lists: The Heart of Your Company’s Direct Mail Marketing Activities 5-5
• Assessing Mailing Lists 5-5
• Elements of a Winning Mailing List 5-6
• Mailing Lists: Self-Compiled and Rented Mailing Lists 5-7
• Self-Compiled Mailing Lists 5-7
• Self-Compiled Mailing List Sources 5-7
• The “Dumb Assistant” List Compiling Method 5-8
• List Compilation: Set Your Database Up Right the First Time 5-10
• Rented Mailing Lists 5-12
• Where to Find Mailing Lists to Rent: SRDS Direct Marketing List Source 5-14
• How to Look for Mailing Lists in SRDS Direct Marketing List Source 5-15
• Types of Trade Publication Mailing Lists 5-16
• Compiled Mailing Lists 5-17
• How Much Response Should You Get from Your Mailings? 5-17
• Mailing List Rentals and Policies 5-18
Part 2: Direct Mail Packages 5-18
• Direct Mail Package Elements 5-20
• Outer Envelope 5-21
• The Sales Letter 5-22
Elements of Successful Direct Mail Sales Letter Copy 5-24
• Lead Paragraph 5-24
• Key Sales Benefits and Sales Bullets 5-24
• Sales Letter Close and Call to Action 5-27
• Layout Tips for Sales Cover Letters 5-28
Brochures for Direct Mail Packages 5-28
Direct Mail Response/Business Reply Cards (BRCs) 5-30
The “Buck Slip” 5-31
The Call to Action: Direct Mail Premiums to Get Inquiries and Orders 5-32
Other Promotional Offers for Direct Mailings 5-33
Self-Mailer Formats: Brochures, #10 Mailers, and Four-Color Postcards 5-34
Self-Mailing Postcards 5-35
Direct Mail Testing: Reducing Risk and Expense in Your Company's Direct Mail Projects (Unit 6)
Typical Mailing Tests 6-2
• When to Test 6-3
• Deciding What to Test 6-3
• Your Testing Benchmarks 6-4
• Testing Sample Sizes: How Small is Too Small and How Big is Too Big? 6-5
• Minimum List Sample Size 6-5
• Finding List Sample Sizes: The “Statistics Professor” Method 6-5
• The “Real World” Sampling Method 6-6
• List-Testing and Sampling: A Typical Example 6-8
Planning Your Direct Mail Test Program 6-10
• Selecting Mailing Lists to Test 6-10
• “Nth-Name” Mailing List Selection 6-11
• Testing Direct Mail Packages 6-11
• Testing Different Promotional Offers 6-12
• Preparing Your Direct Mail Test 6-12
• Create a Test Panel Matrix 6-12
• Key-Coding Your Direct Mail Pieces 6-12
• Developing a Key Code System for Your Mailings 6-13
• Where to Print Key Codes 6-14
• Developing Procedures for Collecting and Reporting Key Codes 6-15
Marketing Professional’s Checklist for Creating a Direct Mail Test Using On-Demand CRM 6-16
1.) Creating a New Campaign Type to Track Mailing List Tests in On-Demand CRM 6-17
2.) Add an Actual Response Calculation Field to Your Campaign Records 6-19
3.) Create a Key Code Field 6-22
4.) Create a New Campaign for Each Mailing List Test and Import or Assign Each Mailing List to Each Campaign 6-22
5.) Capture Responses as they are Received from Your Test Mailings 6-23
6.) Set Up On-Demand CRM Reporting Features to Track and Measure Your Test Mailings 6-24
Developing a Response Curve for Your Mailings 6-24
Analyzing Results of Your Test Mailings 6-29
Direct Mail Troubleshooting: What To Do If Your Test Mailings Fail 6-31
Testing is a Continuous Process: Test Always, and Test Often 6-34
Rolling Out: Scaling Up Your Mailings After Your Direct Mail Tests 6-34
Scaling Up: Determining Your Range of Response to a Mailing 6-34
Test Mailing Rollouts: How Many Pieces to Mail Next? 6-35
Extending Your Direct Mail Program: Timing and Execution 6-37
Direct Mail Execution: Creating, Developing, and Executing Successful Direct Mail Projects (Unit 7)
Putting Direct Mail to Work: A Mailing for Most Every Marketing Situation 7-1
• Situation #1: Mailings to Rented Mailing Lists 7-2
• Marketing Situation #2: Tactical Mailings for Sales Promotions, New Product Announcements,
and Other “Targets of Opportunity” 7-6
• Marketing Situation #3: Inquiry-Generation Postcard Decks 7-7
• Marketing Situation #4: The Sales Rep’s Sales Kit 7-12
• Marketing Situation #5: Sales Inquiry Bounceback Package 7-13
Executing Your Company’s Direct Mail Projects 7-15
• Step 1: Mailing List Selection (Estimated Execution Time: 1- 2 Weeks) 7-16
• Internal Mailing Lists 7-17
• External Mailings: List Execution for Rented Mailing Lists 7-18
• Step 2 : Direct Mail Package Design, Copy and Production (Estimated Execution Time: 1-3 Weeks) 7-21
• Direct Mail Package Development for New Mailings 7-21
Direct Mail Piece Development and Production: Timing and Mechanics 7-22
• Step 1: Sketch Out the Requirements and Sales Copy Points of Your Direct Mail Package 7-23
• Step 2: Direct Mail Package Copy, Development and Production 7-24
• The Proofing Cycle 7-24
• Step 3: The Print Production Process 7-26
• Step 4: Lettershop and Mailing 7-27
• Mailing List Processing 7-29
Marketer’s Action Plan (MAP): Checklist for Executing Direct Mail Campaigns in On-Demand CRM 7-31
1.) Create Your Plan 7-31
2.) Plan for Measurement 7-31
4.) Track, Measure, and Assess 7-34
5.) Evaluate, Adapt, and Improve 7-34
6.) Follow Through 7-34
Trade Show Marketing: Making a Success of Your Company's Trade Show Opportunities (Unit 8)

Figure 8-4: "Trade Show Booth Visibility," from Trade Show Marketing (Unit 8)
Trade Shows: Where Markets Come Alive 8-1
• Trade Shows Keep Marketing Professionals Sharp 8-2
• Locating the Best Trade Shows in Your Market 8-2
Trade Show Timing and Planning 8-3
• Evaluating Trade Show Opportunities 8-4
• Selecting a Trade Show Booth: Location and Size 8-5
• Choosing the Best Trade Show Booth Location 8-5
• Selecting Your Booth Size 8-7
• Getting Your Company Into the Show 8-8
• Trade Show Booth Options 8-9
• Trade Show Booth Backdrop 8-9
How Show Attendees Wander a Trade Show—and How to Get Them to Your Booth 8-11
Producing Your Company’s Trade Show Backdrop Design 8-12
Small Booth Aisle Signs 8-15
Trade Show Sales Video on Flat-Panel Display 8-19
Trade Show Pre-Marketing: What to Do Before the Show 8-21
• Trade Show Postcard Mailings 8-22
• E-Mailing Show Announcements/Invitations to Existing Sales Prospects 8-25
• Advertising in Trade Show Dailies 8-26
• Printed Marketing Collateral for Trade Shows 8-26
• Trade Show Premiums and Drawings 8-28
• Trade Show Logistics 8-28
• Getting Your Booth and Materials to the Show 8-30
• Booth Setup Day 8-31
• Major Trade Show Emergencies 8-32
The Show Begins: How to Work a Trade Show 8-33
When the Show Ends 8-34
Marketer’s Action Plan (MAP): Checklist for Executing Trade Show Campaigns in On-Demand CRM 8-34
1.) Create Your Plan 8-34
Preparation (for Execution) 8-35
Concept and Production 8-35
Pre-Show Promotion 8-36
2.) Plan for Measurement 8-37
Cost Side 8-37
Estimated Revenue Side 8-37
Preparation (Measurement) 8-38
3.) Execute 8-38
Pre-Show 8-38
At the Show 8-39
4.) Track, Measure, and Assess 8-39
5.) Evaluate, Adapt, and Improve 8-39
6.) Follow Through 8-40
Print Advertising Planning and Execution: Making Trade Print Advertising Pay Off in Your Company's Marketing Program (Unit 9)

Figure 9-5: "Fractional Ads," from Print Advertising (Unit 9)
The Trouble with Print Advertising in B2B: Cost and Long Lead Times 9-1
• Should Your Company Be Advertising at All? 9-2
Key Elements of Your Company’s Print Advertising Program 9-4
• Your Advertising Program’s Goals 9-4
• Planning Your Company’s Print Advertising Programs 9-5
1. The Advertising Layout, or Deliverable 9-5
• What’s Your Offer? 9-6
• Always Test Every New Advertising Program 9-6
• Whenever You Run an Ad, Track It 9-7
2. Ad Size: What’s Best for Your Advertising Program? 9-8
• The Full-Page Ad Myth 9-8
• Don’t Run a Full Page Ad When a Smaller Size Will Do 9-10
• Sales vs. Inquiries from the Ad: Best Fractional Ad Sizes 9-12
3. Publication (Trade Media) Choices: Where to Advertise? 9-12
• Trade Media Placement in Your Industry: Usually, Two Publications Rule 9-12
• Standard Rate & Data Service (SRDS) 9-13
• How to Select Publications 9-13
• Media Kits and Sample Issues 9-14
4. Frequency: How Often Should We Advertise? 9-17
• Other Advertising Planning Issues: Ad Scheduling, Positioning and Tracking Response 9-18
• Your Advertising Schedule 9-18
• Display Advertising Positioning 9-19
• Getting the Best Ad Position in a Publication 9-20
• Publication Editorial Schedules 9-20
Using On-Demand CRM to Track Your Ad Placement Schedule 9-21
Planning and Executing a New Print Advertising Campaign
Overview of Key Elements 9-23
Advertising Creative Development and Production (1-4 Weeks) 9-24
Step 1—Your De-Brief to the Agency 9-24
Step 2—The Ad Agency Presentation 9-24
Step 3—Final Ad Production (1 Week) 9-26
Step 4—Space Reservations and Ad Submissions (Less than 1 Week) 9-26
Ad Materials Submission 9-28
Marketer’s Action Plan (MAP): Checklist for Executing Print Advertising Campaigns in On-Demand CRM 9-29
1.) Create Your Plan 9-29
Your Objectives 9-29
Targeting 9-29
Preparation (for Execution) 9-30
Concept and Production 9-30
2.) Plan for Measurement 9-31
Cost Side 9-31
Estimated Revenue Side 9-31
Preparation (Measurement) 9-31
3.) Execute 9-32
4.) Track, Measure, and Assess 9-32
5.) Evaluate, Adapt, and Improve 9-32
6.) Follow Through 9-33
Video and Multimedia: Using the Power of Spoken Words and Moving Images to Sell Your Company's Products (Unit 10)

Figure 10-7: "On-Screen Text Reinforces Your Product's Key Sales Benefits," from Video and Multimedia (Unit 10)
Typical Video and Multimedia Applications 10-1
• High-End Vs. “Industrial” Video Projects 10-3
• The Desktop Video Revolution 10-4
The Video Producer 10-5
• How to Evaluate the Producer’s Demo Reel 10-6
• How to be Your Own Executive Producer 10-6
• Decide on Your Video Project’s Application and Goals 10-7
Web Video 10-7
• Uses for Web Video in B2B Marketing 10-8
• Production Techniques for Web Video 10-9
Every Effective Web Video Begins With a Great Script 10-10
• Web Video Script Structure 10-10
• Visuals and Production Techniques for Web Video 10-11
Trade Show Booth Videos 10-12
Sales Videos 10-12
Video News Releases 10-13
Writing The Script: What Marketing Managers Should Know 10-14
• What to Look for in a Video Script 10-15
• Basic Sales Video Script Structure 10-21
Your Video Production Checklist: Executing Video Projects 10-22
Basic Elements of a Video Project 10-22
The Final Edit: Working with a Video Producer 10-24
Keyword Search Advertising: Generating Keyword Search Leads With Google AdWords (Unit 11)
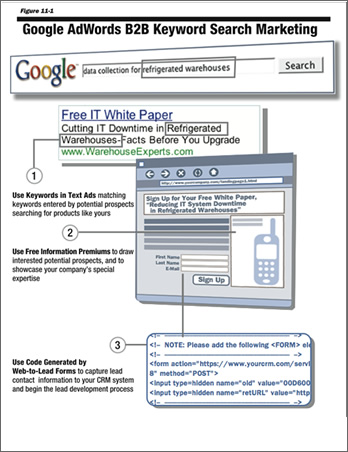
Figure 11-1: "Google AdWords B2B Keyword Search Marketing," from Keyword Search Advertising (Unit 11)
Google AdWords Keyword Search Advertising 11-2
Google AdWords: An Overview 11-4
• AdWords Elements and Terminology 11-5
Developing Content-Based Premiums: The Starting Point for Effective AdWords Search Marketing Programs in B2B 11-8
• What Do Your Prospects Want, and What Does Your Company Know that Gives Prospects What They Want? 11-9
1.) Defining Your Potential Prospect’s Wants, Problems, and Issues 11-10
2.) Assessing and Presenting What Your Company Knows that Solves Your Potential Prospect’s Problem 11-11
3.) Developing Content that Motivates Searchers to Become Prospects 11-13
4.) Finding the Keywords Your Potential Prospects Use to Search for Products Like Yours, or Problems Solved by Your Product 11-14
Developing and Discovering Keywords to Use in Your Search Marketing Program 11-15
• Keywords Describing Your Product 11-16
• Keywords Describing the Problem Solved by Your Product 11-17
• Keywords for Market Segments and Specialized Applications 11-18
• Creating Keyword Lists and Organizing them into Keyword Stacks 11-19
• Specifying Keyword Variations 11-20
• Using Google’s Keyword Tool 11-22
Writing and Placing Text Ads for Google AdWords Programs 11-23
• Google Text Ad Format 11-24
• Writing Google Text Ads 11-24
• How to Begin: Write Copy for the Product, the Premium, or the Problem 11-25
• Text Ad Examples: Product, Premium, and Problem 11-25
• Google Text Ad Copywriting, Targeting, and Execution Tips 11-27
Developing Landing Pages for Google AdWords Lead-Generation Programs 11-29
Thank You Page 11-31
Tracking AdWords Conversions: Adding On-Demand CRM “Web-to-Lead” Tracking to Your Landing Pages 11-31
Executing AdWords Keyword Search Marketing Programs 11-33
Overview: Checklist for Setting Up and Running a New Google AdWords Ad Group 11-33
Troubleshooting Low Response in AdWords B2B Keyword Search Marketing programs 11-36
• Impressions and Low Click-Through Rates 11-36
• Conversions 11-37
E-Mail Lead Development Programs: Developing Effective E-Mail Content for Lead Development Programs (Unit 12)
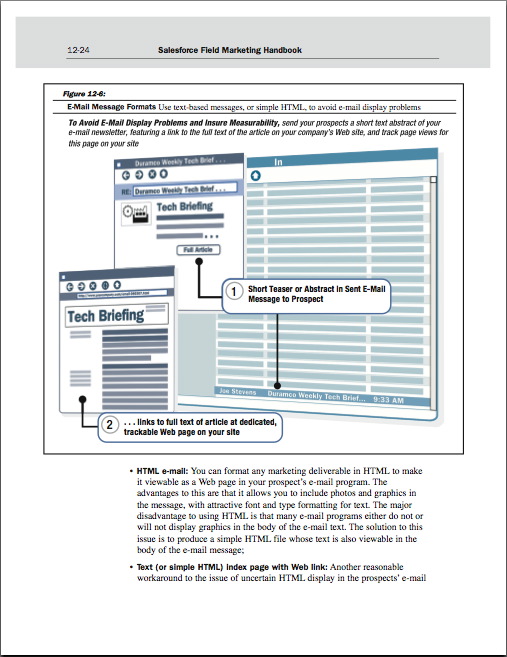
Figure 12-6: "E-Mail Message Formats," from E-Mail Lead Development Programs (Unit 12)
Elements of Successful E-Mail Lead Development Programs 12-2
Major Types of E-Mail Messaging Programs for Lead Development 12-3
E-Mail Message Templates for Every Selling Situation 12-6
• Sales Letter and Message Template Examples 12-7
• Guidelines for Writing E-Mail Sales Letter Templates 12-8
Editorial E-Mail 12-10
• The Importance of Being a Thought Leader 12-10
• Benefits of an Editorial E-Mail Messaging Program 12-11
I: Recognizing Your Company’s Special Expertise: “Show What You Know” 12-11
• Finding and Developing Content for Editorial E-Mail Messaging Programs:
• Where to Look and How to Start 12-14
• Examples of Editorial E-Mail Message Programs 12-15
II: Developing Your Company’s Expertise to Create Editorial E-Mail Messaging Programs: “Show What You Know” 12-16
• Observing Your Industry’s Issues, Trends, and Motivations 12-16
• Finding and Evaluating Available Content for Your Editorial E-Mail Program 12-18
• Sources Within Your Company 12-19
• B2B Editorial Examples 12-20
• Developing Editorial Content for Your E-Mail Messaging Program 12-21
• Editorial E-Mail Formats 12-21
• Editorial Content Formats 12-22
• E-Mail Message Formats 12-23
• E-Mail Message Formats: Which Format to Use? 12-25
Developing Content Targeted to Other Decision-Makers at the Prospect’s Company 12-25
Writing and Producing Content for Your Editorial E-Mail Messaging Program 12-26
Lead Development Programs: Executing Effective E-Mail Messaging with Integrated Lead Development Programs (Unit 13)
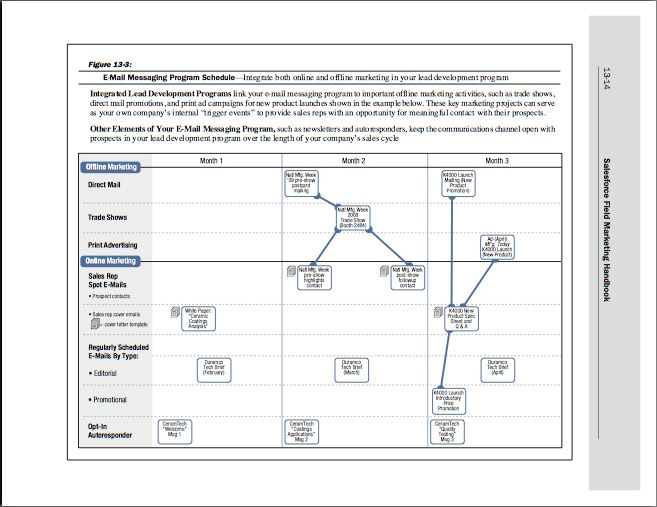
Figure 13-3 "E-Mail Messaging Program Schedule," from Lead Development Programs (Unit 13)
Timing and Scheduling of E-Mail Message Transmissions 13-2
Scheduled And Ad Hoc, “Spot” Transmissions By Sales Reps 13-2
• Examples of “Triggering Events” that Increase Selling Opportunities 13-2
• Marketing’s Response to “Triggering Events” in the Lead Development Process 13-3
Scheduled E-Mail Message Transmissions 13-5
• Editorial E-Mail Content 13-5
• E-Mail Prospect Newsletters 13-5
Targeted or Scheduled Promotional E-Mail Announcements 13-7
Sequenced Autoresponder E-Mail Message Transmissions 13-8
• Sequenced Autoresponder Applications for B2B Lead Development Programs 13-9
• Sequenced Autoresponder Programs: Factors to Consider 13-10
• Content Selection Decisions for Sequenced Autoresponder Mailings 13-11
Managing, Measuring, and Adapting Your E-Mail Messaging Programs 13-13
Creating an E-Mail Messaging Schedule for Your E-Mail Messaging Program 13-13
Execution of E-Mail Messaging Programs 13-15
Targeting Content to Prospects Throughout Your Company’s Sales Cycle 13-17
Tracking and Measuring Your E-Mail Messaging Program 13-18
• Common E-Mail Measurements 13-18
• Deliverability Rate 13-18
• Open Rate 13-19
• Click-Through Rate 13-19
• Forms Completion (or Download) Rate 13-20
• Opt-In Rate or Unsubscribe Rate 13-21
• Observing, Assessing, and Comparing Key E-Mail Measurement Rates 13-21
Start-Up Marketing: Marketing for Start-Ups, New Product Launches, and New Markets (Unit 14)

Figure 14-4: "Private Label and Co-Marketing Deals," from Start-Up Marketing (Unit 14)
Riding the Tiger 14-1
• Markets Turn on a Dime in Every Start-Up or New Product Launch—So Be Ready 14-2
• Marketing in Start-Ups and New Product Launches Means Continuous Testing 14-2
• The Federal Express Story: Fast Response and Marketing Execution Saves the Day 14-3
Start-Up and New Product Marketing: The Important Thing is Knowing What You Don’t Know 14-5
• Marketing Assumptions Used for a Start-Up’s Financial Projections 14-6
• Estimating Market Response Before Market-Testing Your Product 14-6
Step 1: Market Gap Analysis 14-9
Step 2: General Market Assessment Checklist 14-10
Start-Up Marketing Manager’s Analysis and Action Plan 14-10
1.) General Issues 14-11
2.) Background Research and Action Items 14-11
3.) Marketing Deliverables 14-13
Development of Rough Marketing Deliverables for Market Testing 14-14
4.) Market testing 14-16
5.) Targets of Opportunity 14-17
Marketing Turnarounds: When Your Marketing Program Hits the Wall: Troubleshooting and Correcting Poor Sales Response (Unit 15)

Figure 15-2: "In The Arena," from Marketing Turnarounds (Unit 15)
Landing in the Grey Middle 15-1
• There’s Always Something You Can Do 15-2
• What Went Right? 15-3
Examining Where Marketing Projects Go Wrong: Common Causes of Poor Marketing Response 15-5
• Marketing-Related Problems 15-5
• Copy and Deliverable Problems 15-5
• Market and Prospect Selection 15-8
• Direct Mail 15-8
• Sales Support 15-10
• Print Advertising 15-11
• Clarity 15-13
•Boldness 15-14
Marketing Execution 15-16
• Solving Execution Problems 15-17
Product-Related Problems 15-19
• More and Better Marketing Skill Never Saved a Bad Product 15-19
• How to Get Product Feedback 15-20
• Common Product-Related Causes of Poor Market Response 15-20
• Crisis Marketing: Taking Action When the Product is Ahead of Its Time 15-22
• Saving a Product That is Ahead of its Time 15-23
• Common Changes to Marketing Strategy and Deliverables When a Product is Retooled 15-24
Distribution and Market Size Problems 15-25
• Common Distributor Problems 15-25
• Solving Distributor Problems 15-26
• Sales Meetings 15-26
• Adding and Improving Distributor Sales and Marketing Deliverables 15-28
• Greater Involvement, Training and Communication Improve Distributor Sales Performance 15-29
Uncontrollable Factors Revealed by Your Test 15-30
Action is the Cure for Adverse Market Conditions 15-31

